Dynamic Filtering in Claude Web Search: Faster, Cheaper
Dynamic Filtering in Claude Web Search: Faster, Cheaper
Claude
Antropico
17 feb 2026


¿No sabes por dónde empezar con la IA?
Evalúa preparación, riesgos y prioridades en menos de una hora.
¿No sabes por dónde empezar con la IA?
Evalúa preparación, riesgos y prioridades en menos de una hora.
➔ Descarga nuestro paquete gratuito de preparación para IA
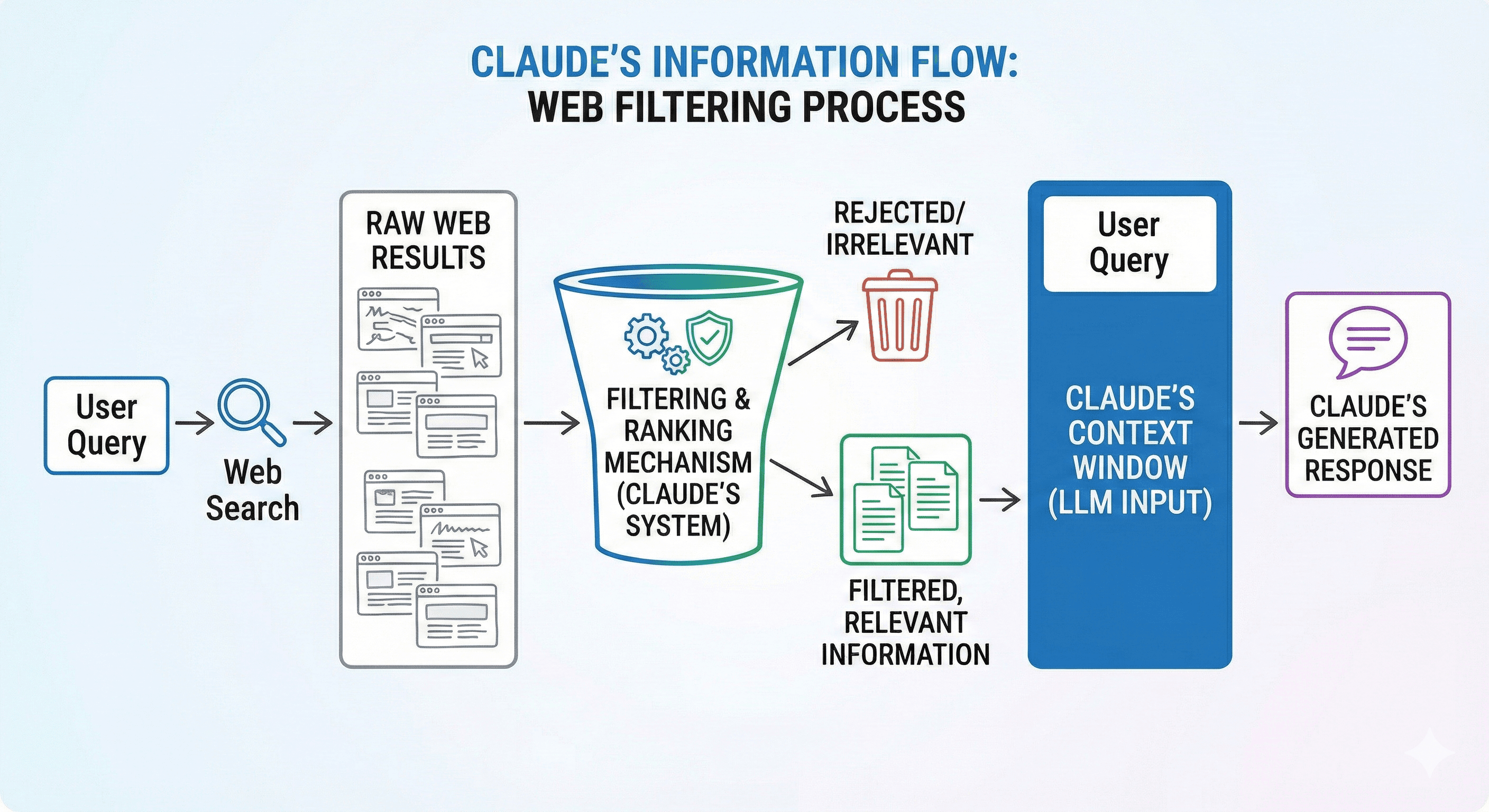
Dynamic filtering in Claude’s web search lets the model write and execute code to trim search results before they enter the context window. That means Claude reads less irrelevant content, which can improve search accuracy (about 11% on benchmarks) while using fewer input tokens (about 24%). It’s available via the Claude API web search and web fetch tools.
Web search is one of the quickest ways to make an AI assistant more useful—and one of the easiest ways to make it waste tokens. Traditional “browse then summarise” flows pull a lot of raw HTML into the context window, and much of it isn’t relevant to the question you’re trying to answer.
Anthropic’s latest update tackles that problem directly. Claude’s web search and web fetch tools can now automatically write and execute code to post-process results before they enter the context window, keeping only what matters and discarding the rest. Anthropic reports this improves performance on agentic search benchmarks by ~11% on average, while using ~24% fewer input tokens.
Why this matters now
If you’re building anything beyond a toy demo—research agents, citation checkers, “answer from docs” assistants, or competitive intelligence bots—you’ll recognise the trade-offs:
Too much context can dilute relevance and increase hallucination risk.
Too many tokens can make an otherwise-good workflow too expensive to run at scale.
Messy web pages (navigation, cookie banners, unrelated sections) often swamp the useful parts.
Dynamic filtering is a pragmatic solution: treat web results like raw data, run a quick processing step, then pass only the cleaned output into Claude’s reasoning step.
What’s actually new: dynamic filtering inside web search and web fetch
In the updated flow, Claude can:
Run a web search (or fetch a page).
Generate a small script to extract the relevant parts (for example: headings, pricing tables, a specific paragraph, or citation candidates).
Execute that script in a sandboxed code execution environment.
Only send the filtered output into the context window for final reasoning and writing.
Anthropic describes this as filtering “before loading results into context”, rather than asking the model to reason over full HTML.
The headline results
Anthropic evaluated web search on Sonnet 4.6 and Opus 4.6 with and without dynamic filtering (and no other tools enabled). Across BrowseComp and DeepsearchQA, dynamic filtering improved performance by an average of 11%, while using 24% fewer input tokens.
They also share DeepsearchQA F1 improvements (for example, Sonnet 4.6 moving from 52.6% to 59.4%, and Opus 4.6 from 69.8% to 77.3%).
Practical note: token costs can still vary based on how much code Claude writes to do the filtering, so it’s worth testing against your own real queries.
How to enable dynamic filtering via the Claude API
Dynamic filtering is supported in the latest web search tool version: web_search_20260209. The Claude API docs explicitly note that this version supports dynamic filtering for Opus 4.6 and Sonnet 4.6, and that Claude can write and execute code to filter results before they reach the context window.
What you’ll need:
Tool version:
web_search_20260209(and/orweb_fetch_20260209)Beta header:
anthropic-beta: code-execution-web-tools-2026-02-09Code execution tool enabled, because dynamic filtering depends on it.
Cost and governance considerations you should know
One helpful detail: Anthropic states that code execution is free when used with web search or web fetch—i.e., there are no additional charges for code execution tool calls beyond standard input/output token costs when those web tools are included.
There are also important policy nuances:
The web search tool page notes dynamic filtering and includes ZDR eligibility (where applicable).
The code execution tool page notes code execution capabilities and that some arrangements may differ for retention depending on feature use—so it’s worth aligning with your organisation’s security posture early.
When dynamic filtering delivers the most value
You’ll get the biggest uplift when the “raw web” is noisy or large, for example:
Technical documentation searches where you only need a specific section or parameter definition.
Literature review and citation verification, where you want to extract and compare multiple sources quickly.
Multi-step research (the kind that usually explodes token usage because every step drags more pages into context).
If your current approach involves “search → fetch 5 pages → dump HTML into context”, dynamic filtering is a straightforward upgrade.
A practical implementation pattern (what to build)
Here’s a clean pattern we see working well in production:
Write prompts that declare the extraction goal
Example: “Find the pricing tiers and extract only the pricing table + any footnotes about limits.”Let the tools do the messy work
Use web search + web fetch with dynamic filtering so Claude processes results outside the context window first.Return structured output
Ask Claude to return a table (tiers, limits, sources) or a concise bullet list with citations.Add an evaluation loop
Measure accuracy on your own queries, because your domain will differ from benchmarks. Anthropic recommends evaluating against representative production queries.
How this fits into the bigger “efficient agents” direction
Dynamic filtering is part of a wider shift: keep large, messy intermediate artefacts out of the model’s context window, and only pass through what’s needed to answer the user.
Anthropic’s engineering write-ups on code execution with MCP and advanced tool use describe the same core principle: reduce context bloat, improve orchestration, and let code handle loops, filtering, and transformation where it makes sense.
Summary and next steps
Dynamic filtering makes Claude’s web search more practical at scale: cleaner context, fewer tokens, and better accuracy on search-heavy workflows.
Next steps for teams:
Audit one or two of your most token-hungry search workflows.
Enable
web_search_20260209+ the beta header.Compare accuracy, cost, and latency before/after.
If you want help designing an evaluation plan or rolling this into a governed internal tool, Generation Digital can support implementation and adoption.
FAQ
Q1: How does dynamic filtering improve search accuracy?
By letting Claude post-process search results with code execution before the content enters the context window. That reduces irrelevant text and helps the model focus on what actually answers the question.
Q2: What does “24% fewer input tokens” mean in practice?
It means the model is typically given less raw web content to read because filtering happens first—reducing context bloat and, often, overall cost for search-heavy tasks.
Q3: Is dynamic filtering available to everyone?
It’s available via the Claude API’s newer web search/web fetch tool versions, and Anthropic states it’s enabled by default when using those newer tools with Opus 4.6 and Sonnet 4.6 (subject to tool version and headers).
Q4: How do I enable it?
Use web_search_20260209 (and/or web_fetch_20260209) and include the beta header code-execution-web-tools-2026-02-09. Dynamic filtering requires the code execution tool.
Q5: Does code execution add extra cost?
Anthropic notes that code execution is free when used with web search or web fetch tools (no extra tool-call charges beyond standard token costs).
Dynamic filtering in Claude’s web search lets the model write and execute code to trim search results before they enter the context window. That means Claude reads less irrelevant content, which can improve search accuracy (about 11% on benchmarks) while using fewer input tokens (about 24%). It’s available via the Claude API web search and web fetch tools.
Web search is one of the quickest ways to make an AI assistant more useful—and one of the easiest ways to make it waste tokens. Traditional “browse then summarise” flows pull a lot of raw HTML into the context window, and much of it isn’t relevant to the question you’re trying to answer.
Anthropic’s latest update tackles that problem directly. Claude’s web search and web fetch tools can now automatically write and execute code to post-process results before they enter the context window, keeping only what matters and discarding the rest. Anthropic reports this improves performance on agentic search benchmarks by ~11% on average, while using ~24% fewer input tokens.
Why this matters now
If you’re building anything beyond a toy demo—research agents, citation checkers, “answer from docs” assistants, or competitive intelligence bots—you’ll recognise the trade-offs:
Too much context can dilute relevance and increase hallucination risk.
Too many tokens can make an otherwise-good workflow too expensive to run at scale.
Messy web pages (navigation, cookie banners, unrelated sections) often swamp the useful parts.
Dynamic filtering is a pragmatic solution: treat web results like raw data, run a quick processing step, then pass only the cleaned output into Claude’s reasoning step.
What’s actually new: dynamic filtering inside web search and web fetch
In the updated flow, Claude can:
Run a web search (or fetch a page).
Generate a small script to extract the relevant parts (for example: headings, pricing tables, a specific paragraph, or citation candidates).
Execute that script in a sandboxed code execution environment.
Only send the filtered output into the context window for final reasoning and writing.
Anthropic describes this as filtering “before loading results into context”, rather than asking the model to reason over full HTML.

The headline results
Anthropic evaluated web search on Sonnet 4.6 and Opus 4.6 with and without dynamic filtering (and no other tools enabled). Across BrowseComp and DeepsearchQA, dynamic filtering improved performance by an average of 11%, while using 24% fewer input tokens.
They also share DeepsearchQA F1 improvements (for example, Sonnet 4.6 moving from 52.6% to 59.4%, and Opus 4.6 from 69.8% to 77.3%).
Practical note: token costs can still vary based on how much code Claude writes to do the filtering, so it’s worth testing against your own real queries.
How to enable dynamic filtering via the Claude API
Dynamic filtering is supported in the latest web search tool version: web_search_20260209. The Claude API docs explicitly note that this version supports dynamic filtering for Opus 4.6 and Sonnet 4.6, and that Claude can write and execute code to filter results before they reach the context window.
What you’ll need:
Tool version:
web_search_20260209(and/orweb_fetch_20260209)Beta header:
anthropic-beta: code-execution-web-tools-2026-02-09Code execution tool enabled, because dynamic filtering depends on it.
Cost and governance considerations you should know
One helpful detail: Anthropic states that code execution is free when used with web search or web fetch—i.e., there are no additional charges for code execution tool calls beyond standard input/output token costs when those web tools are included.
There are also important policy nuances:
The web search tool page notes dynamic filtering and includes ZDR eligibility (where applicable).
The code execution tool page notes code execution capabilities and that some arrangements may differ for retention depending on feature use—so it’s worth aligning with your organisation’s security posture early.
When dynamic filtering delivers the most value
You’ll get the biggest uplift when the “raw web” is noisy or large, for example:
Technical documentation searches where you only need a specific section or parameter definition.
Literature review and citation verification, where you want to extract and compare multiple sources quickly.
Multi-step research (the kind that usually explodes token usage because every step drags more pages into context).
If your current approach involves “search → fetch 5 pages → dump HTML into context”, dynamic filtering is a straightforward upgrade.
A practical implementation pattern (what to build)
Here’s a clean pattern we see working well in production:
Write prompts that declare the extraction goal
Example: “Find the pricing tiers and extract only the pricing table + any footnotes about limits.”Let the tools do the messy work
Use web search + web fetch with dynamic filtering so Claude processes results outside the context window first.Return structured output
Ask Claude to return a table (tiers, limits, sources) or a concise bullet list with citations.Add an evaluation loop
Measure accuracy on your own queries, because your domain will differ from benchmarks. Anthropic recommends evaluating against representative production queries.
How this fits into the bigger “efficient agents” direction
Dynamic filtering is part of a wider shift: keep large, messy intermediate artefacts out of the model’s context window, and only pass through what’s needed to answer the user.
Anthropic’s engineering write-ups on code execution with MCP and advanced tool use describe the same core principle: reduce context bloat, improve orchestration, and let code handle loops, filtering, and transformation where it makes sense.
Summary and next steps
Dynamic filtering makes Claude’s web search more practical at scale: cleaner context, fewer tokens, and better accuracy on search-heavy workflows.
Next steps for teams:
Audit one or two of your most token-hungry search workflows.
Enable
web_search_20260209+ the beta header.Compare accuracy, cost, and latency before/after.
If you want help designing an evaluation plan or rolling this into a governed internal tool, Generation Digital can support implementation and adoption.
FAQ
Q1: How does dynamic filtering improve search accuracy?
By letting Claude post-process search results with code execution before the content enters the context window. That reduces irrelevant text and helps the model focus on what actually answers the question.
Q2: What does “24% fewer input tokens” mean in practice?
It means the model is typically given less raw web content to read because filtering happens first—reducing context bloat and, often, overall cost for search-heavy tasks.
Q3: Is dynamic filtering available to everyone?
It’s available via the Claude API’s newer web search/web fetch tool versions, and Anthropic states it’s enabled by default when using those newer tools with Opus 4.6 and Sonnet 4.6 (subject to tool version and headers).
Q4: How do I enable it?
Use web_search_20260209 (and/or web_fetch_20260209) and include the beta header code-execution-web-tools-2026-02-09. Dynamic filtering requires the code execution tool.
Q5: Does code execution add extra cost?
Anthropic notes that code execution is free when used with web search or web fetch tools (no extra tool-call charges beyond standard token costs).
Recibe noticias y consejos sobre IA cada semana en tu bandeja de entrada
Al suscribirte, das tu consentimiento para que Generation Digital almacene y procese tus datos de acuerdo con nuestra política de privacidad. Puedes leer la política completa en gend.co/privacy.
Próximos talleres y seminarios web


Claridad Operacional a Gran Escala - Asana
Webinar Virtual
Miércoles 25 de febrero de 2026
En línea


Trabaja con compañeros de equipo de IA - Asana
Taller Presencial
Jueves 26 de febrero de 2026
Londres, Reino Unido


De Idea a Prototipo: IA en Miro
Seminario Web Virtual
Miércoles 18 de febrero de 2026
En línea
Generación
Digital

Oficina en Reino Unido
Generation Digital Ltd
33 Queen St,
Londres
EC4R 1AP
Reino Unido
Oficina en Canadá
Generation Digital Americas Inc
181 Bay St., Suite 1800
Toronto, ON, M5J 2T9
Canadá
Oficina en EE. UU.
Generation Digital Américas Inc
77 Sands St,
Brooklyn, NY 11201,
Estados Unidos
Oficina de la UE
Software Generación Digital
Edificio Elgee
Dundalk
A91 X2R3
Irlanda
Oficina en Medio Oriente
6994 Alsharq 3890,
An Narjis,
Riad 13343,
Arabia Saudita
Número de la empresa: 256 9431 77 | Derechos de autor 2026 | Términos y Condiciones | Política de Privacidad
Generación
Digital

Oficina en Reino Unido
Generation Digital Ltd
33 Queen St,
Londres
EC4R 1AP
Reino Unido
Oficina en Canadá
Generation Digital Americas Inc
181 Bay St., Suite 1800
Toronto, ON, M5J 2T9
Canadá
Oficina en EE. UU.
Generation Digital Américas Inc
77 Sands St,
Brooklyn, NY 11201,
Estados Unidos
Oficina de la UE
Software Generación Digital
Edificio Elgee
Dundalk
A91 X2R3
Irlanda
Oficina en Medio Oriente
6994 Alsharq 3890,
An Narjis,
Riad 13343,
Arabia Saudita