RAG Models: Enhance Enterprise AI Precision in 2026 for Canadian Businesses
RAG Models: Enhance Enterprise AI Precision in 2026 for Canadian Businesses
Gemini
Confusion
OpenAI
Claude
ChatGPT
Dec 9, 2025
Uncertain about how to get started with AI?Evaluate your readiness, potential risks, and key priorities in less than an hour.
Uncertain about how to get started with AI?Evaluate your readiness, potential risks, and key priorities in less than an hour.
➔ Download Our Free AI Preparedness Pack
Why RAG matters in 2026
RAG has evolved from a promising prototype to a reliable enterprise pattern. In 2026, accuracy isn't just a quality goal; it's a compliance requirement. By basing every answer on cited documents, RAG makes outputs auditable for internal review and external regulators. It also shortens the update cycle: when policies, product specs, or prices change, you update the index instead of retraining a model, allowing teams to respond to change in hours, not months. Equally important, RAG can be cost-effective. Smaller, well-managed models combined with strong retrieval often outperform larger models that rely solely on memory for enterprise Q&A. And because content is stored within controlled indices, you can enforce access rules, redact sensitive information, and keep data within your selected region, incorporating privacy by design into daily operations.
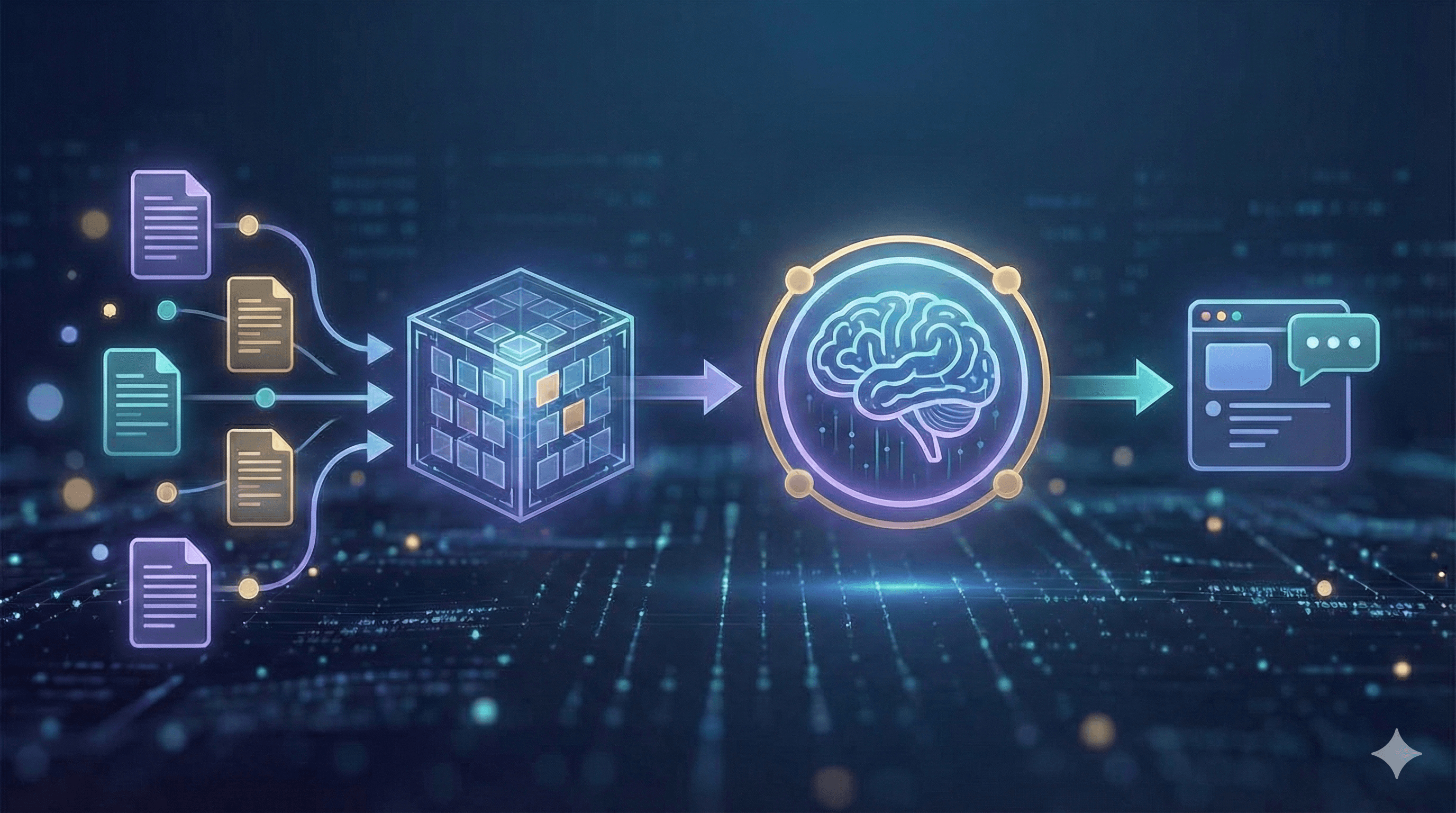
How RAG works (modern view)
A modern RAG system starts with ingestion: you register the sources that matter — policies, wikis, tickets, PDFs, and structured data — then clean, deduplicate, and label them with useful metadata such as owner, date, and region. Next is chunking and embedding. Rather than slicing text arbitrarily, you preserve headings and sections so each piece carries enough context to be meaningful, then store embeddings in a secure vector index alongside keyword fields for exact matches.
At query time, the assistant retrieves a small set of promising passages using hybrid search that blends semantic vectors with classic keyword filters (for SKUs, acronyms, and dates). A lightweight re-ranker can reorder these candidates so only the most relevant five or six are selected. The system then augments the prompt with those passages, instructions, and guidelines (for example: answer concisely, cite sources, and refuse if evidence is missing). A governed LLM generates the reply and returns the citations and deep links so users can inspect the originals. Finally, you evaluate and monitor continuously — tracking accuracy, latency, and cost with automated tests, and reviewing samples by hand to maintain high quality.
Key benefits
Enterprises adopt RAG for four main reasons. First, answers are accurate and current because they are grounded in the latest documents instead of a model's outdated memory. Second, maintenance is reduced: you update an index, not a model, which is ideal for rapidly changing policies and product data. Third, RAG provides verifiable provenance — citations enable employees and customers to verify claims with a click. Fourth, you achieve configurable privacy via role-based access, redaction, and audit logs, keeping sensitive information within your environment.
Architecture patterns
Start with classic RAG — vector search returns top-k passages that you pass to the model. It's fast and sets a measurable baseline. Most enterprises quickly shift to hybrid RAG, combining vectors with keyword filters and metadata facets to manage elements like part numbers and effective dates. When quality must be maximized, introduce a re-ranked pipeline: retrieve broadly (e.g., k≈50) and let a cross-encoder promote the best five to the prompt.
For complex questions, multi-hop or agentic retrieval plans a short search journey — reading a policy, following an exception, then opening the relevant form. Finally, structured RAG mixes unstructured text with tables and JSON, allowing the assistant to call tools or SQL for facts instead of paraphrasing numbers from prose.
Practical steps
1) Data preparation
Start with a source registry to identify which SharePoint sites, Drives, Confluence spaces, ticket queues, and product databases will feed the assistant. Preserve headings, lists, and tables during conversion, strip out boilerplate and signatures, and chunk content into sections of 200–600 tokens that inherit their parent headers. Attach metadata such as owner, product, region (Canada/EU), effective date, and security label. For personal data, minimize or redact before indexing and document the legal basis for processing.
2) Retrieval & prompting
Use hybrid search (BM25 plus vectors) and apply filters like region:Canada or status:current. Make the system prompt specific: “Answer only from the provided context; include citations; if evidence is missing, say ‘Not found’.” Limit context to a few high-quality passages rather than many noisy ones to reduce both latency and hallucinations.
3) Evaluation & monitoring
Assemble a gold set of representative questions with accurate answers and references, then track faithfulness, context precision/recall, answer relevance, latency, and cost. In production, collect thumbs-up/down with reasons and analyze “no answer” events for coverage gaps. Deploy changes behind release gates — for example, faithfulness ≥95% and hallucinations ≤2% on your set — to ensure quality doesn’t degrade for users.
4) Governance & security (Canada/EU aware)
Protect indices with role-based access and attribute rules for sensitive collections. Log queries and retrieved documents with a retention policy aligned to local regulations, and be transparent with users: a brief disclosure such as “Answers are generated from internal documents dated [range]” sets expectations and builds trust.
Example use cases
An employee helpdesk becomes truly self-serve when HR and IT policies are accessible by title, topic, and effective date, with each answer citing the exact clause. Field sales teams can inquire about product specs, pricing rules, and competitor comparisons; answers are sourced from battlecards and release notes, helping reps stay consistent without memorizing everything. In customer service, assistants present warranty terms, known issues, and step-by-step solutions, enabling agents to resolve tickets faster and escalate fewer. For risk and compliance, RAG supports policy lookups with clear exception handling and approval routes, reducing back-and-forth and audit risks.
Mini-playbooks
A. Policy assistant (2 weeks). Start by ingesting HR and IT policies (PDF/HTML) along with a change log and named owners. Configure hybrid retrieval with a small re-ranker and a grounding prompt that enforces citations and refusal when evidence is absent. Build an evaluation set of ~100 representative questions, then pilot with a single department. Aim for ≥90% helpfulness, ≤2% hallucination, and mean latency under 2.5 seconds before you expand.
B. Product knowledge bot (3 weeks). Combine documents, specs, SKUs, and release notes. Use schema-aware chunking so tables and attributes remain queryable, and add a tool that can execute simple SQL for prices or dimensions. Guard generation with strict instructions and log every answer with sources. Success looks like reduced time-to-answer for reps and higher ticket deflection in support.
Next Steps
RAG provides your enterprise assistants with a reliable memory — delivering answers sourced from approved documents, updated in hours rather than months, and complete with citations. Start with a small, high-value domain (policies or products), measure accuracy, and scale up.
Interested in a pilot within 2–3 weeks? Generation Digital can assist with architecture, data preparation, evaluation, and governance.
FAQs
What is a RAG model?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation pairs search over your documents with a generative model. The model answers using retrieved passages and provides citations.
How do RAG models benefit enterprises?
They reduce retraining needs, increase accuracy, and provide verifiable answers — ideal for policy, product, and knowledge management use cases.
Does RAG replace long-context models?
No. While long context is beneficial, RAG is essential for freshness, access control, and explainability.
What tools do we need?
A document store or data lake, a vector+keyword search service, an embedding model, an LLM, and observability (evaluation + logs).
How do we keep data safe?
Apply role-based access to collections, redact sensitive fields, and store indices within your cloud region (e.g., Canada or EU).
Why RAG matters in 2026
RAG has evolved from a promising prototype to a reliable enterprise pattern. In 2026, accuracy isn't just a quality goal; it's a compliance requirement. By basing every answer on cited documents, RAG makes outputs auditable for internal review and external regulators. It also shortens the update cycle: when policies, product specs, or prices change, you update the index instead of retraining a model, allowing teams to respond to change in hours, not months. Equally important, RAG can be cost-effective. Smaller, well-managed models combined with strong retrieval often outperform larger models that rely solely on memory for enterprise Q&A. And because content is stored within controlled indices, you can enforce access rules, redact sensitive information, and keep data within your selected region, incorporating privacy by design into daily operations.
How RAG works (modern view)
A modern RAG system starts with ingestion: you register the sources that matter — policies, wikis, tickets, PDFs, and structured data — then clean, deduplicate, and label them with useful metadata such as owner, date, and region. Next is chunking and embedding. Rather than slicing text arbitrarily, you preserve headings and sections so each piece carries enough context to be meaningful, then store embeddings in a secure vector index alongside keyword fields for exact matches.
At query time, the assistant retrieves a small set of promising passages using hybrid search that blends semantic vectors with classic keyword filters (for SKUs, acronyms, and dates). A lightweight re-ranker can reorder these candidates so only the most relevant five or six are selected. The system then augments the prompt with those passages, instructions, and guidelines (for example: answer concisely, cite sources, and refuse if evidence is missing). A governed LLM generates the reply and returns the citations and deep links so users can inspect the originals. Finally, you evaluate and monitor continuously — tracking accuracy, latency, and cost with automated tests, and reviewing samples by hand to maintain high quality.
Key benefits
Enterprises adopt RAG for four main reasons. First, answers are accurate and current because they are grounded in the latest documents instead of a model's outdated memory. Second, maintenance is reduced: you update an index, not a model, which is ideal for rapidly changing policies and product data. Third, RAG provides verifiable provenance — citations enable employees and customers to verify claims with a click. Fourth, you achieve configurable privacy via role-based access, redaction, and audit logs, keeping sensitive information within your environment.
Architecture patterns
Start with classic RAG — vector search returns top-k passages that you pass to the model. It's fast and sets a measurable baseline. Most enterprises quickly shift to hybrid RAG, combining vectors with keyword filters and metadata facets to manage elements like part numbers and effective dates. When quality must be maximized, introduce a re-ranked pipeline: retrieve broadly (e.g., k≈50) and let a cross-encoder promote the best five to the prompt.
For complex questions, multi-hop or agentic retrieval plans a short search journey — reading a policy, following an exception, then opening the relevant form. Finally, structured RAG mixes unstructured text with tables and JSON, allowing the assistant to call tools or SQL for facts instead of paraphrasing numbers from prose.
Practical steps
1) Data preparation
Start with a source registry to identify which SharePoint sites, Drives, Confluence spaces, ticket queues, and product databases will feed the assistant. Preserve headings, lists, and tables during conversion, strip out boilerplate and signatures, and chunk content into sections of 200–600 tokens that inherit their parent headers. Attach metadata such as owner, product, region (Canada/EU), effective date, and security label. For personal data, minimize or redact before indexing and document the legal basis for processing.
2) Retrieval & prompting
Use hybrid search (BM25 plus vectors) and apply filters like region:Canada or status:current. Make the system prompt specific: “Answer only from the provided context; include citations; if evidence is missing, say ‘Not found’.” Limit context to a few high-quality passages rather than many noisy ones to reduce both latency and hallucinations.
3) Evaluation & monitoring
Assemble a gold set of representative questions with accurate answers and references, then track faithfulness, context precision/recall, answer relevance, latency, and cost. In production, collect thumbs-up/down with reasons and analyze “no answer” events for coverage gaps. Deploy changes behind release gates — for example, faithfulness ≥95% and hallucinations ≤2% on your set — to ensure quality doesn’t degrade for users.
4) Governance & security (Canada/EU aware)
Protect indices with role-based access and attribute rules for sensitive collections. Log queries and retrieved documents with a retention policy aligned to local regulations, and be transparent with users: a brief disclosure such as “Answers are generated from internal documents dated [range]” sets expectations and builds trust.
Example use cases
An employee helpdesk becomes truly self-serve when HR and IT policies are accessible by title, topic, and effective date, with each answer citing the exact clause. Field sales teams can inquire about product specs, pricing rules, and competitor comparisons; answers are sourced from battlecards and release notes, helping reps stay consistent without memorizing everything. In customer service, assistants present warranty terms, known issues, and step-by-step solutions, enabling agents to resolve tickets faster and escalate fewer. For risk and compliance, RAG supports policy lookups with clear exception handling and approval routes, reducing back-and-forth and audit risks.
Mini-playbooks
A. Policy assistant (2 weeks). Start by ingesting HR and IT policies (PDF/HTML) along with a change log and named owners. Configure hybrid retrieval with a small re-ranker and a grounding prompt that enforces citations and refusal when evidence is absent. Build an evaluation set of ~100 representative questions, then pilot with a single department. Aim for ≥90% helpfulness, ≤2% hallucination, and mean latency under 2.5 seconds before you expand.
B. Product knowledge bot (3 weeks). Combine documents, specs, SKUs, and release notes. Use schema-aware chunking so tables and attributes remain queryable, and add a tool that can execute simple SQL for prices or dimensions. Guard generation with strict instructions and log every answer with sources. Success looks like reduced time-to-answer for reps and higher ticket deflection in support.
Next Steps
RAG provides your enterprise assistants with a reliable memory — delivering answers sourced from approved documents, updated in hours rather than months, and complete with citations. Start with a small, high-value domain (policies or products), measure accuracy, and scale up.
Interested in a pilot within 2–3 weeks? Generation Digital can assist with architecture, data preparation, evaluation, and governance.
FAQs
What is a RAG model?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation pairs search over your documents with a generative model. The model answers using retrieved passages and provides citations.
How do RAG models benefit enterprises?
They reduce retraining needs, increase accuracy, and provide verifiable answers — ideal for policy, product, and knowledge management use cases.
Does RAG replace long-context models?
No. While long context is beneficial, RAG is essential for freshness, access control, and explainability.
What tools do we need?
A document store or data lake, a vector+keyword search service, an embedding model, an LLM, and observability (evaluation + logs).
How do we keep data safe?
Apply role-based access to collections, redact sensitive fields, and store indices within your cloud region (e.g., Canada or EU).
Receive weekly AI news and advice straight to your inbox
By subscribing, you agree to allow Generation Digital to store and process your information according to our privacy policy. You can review the full policy at gend.co/privacy.
Generation
Digital

Business Number: 256 9431 77 | Copyright 2026 | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
Generation
Digital