GABRIEL Toolkit: Scale Qualitative Research with GPT
GABRIEL Toolkit: Scale Qualitative Research with GPT
OpenAI
Feb 13, 2026


Uncertain about how to get started with AI?
Evaluate your readiness, potential risks, and key priorities in less than an hour.
Uncertain about how to get started with AI?
Evaluate your readiness, potential risks, and key priorities in less than an hour.
➔ Download Our Free AI Preparedness Pack
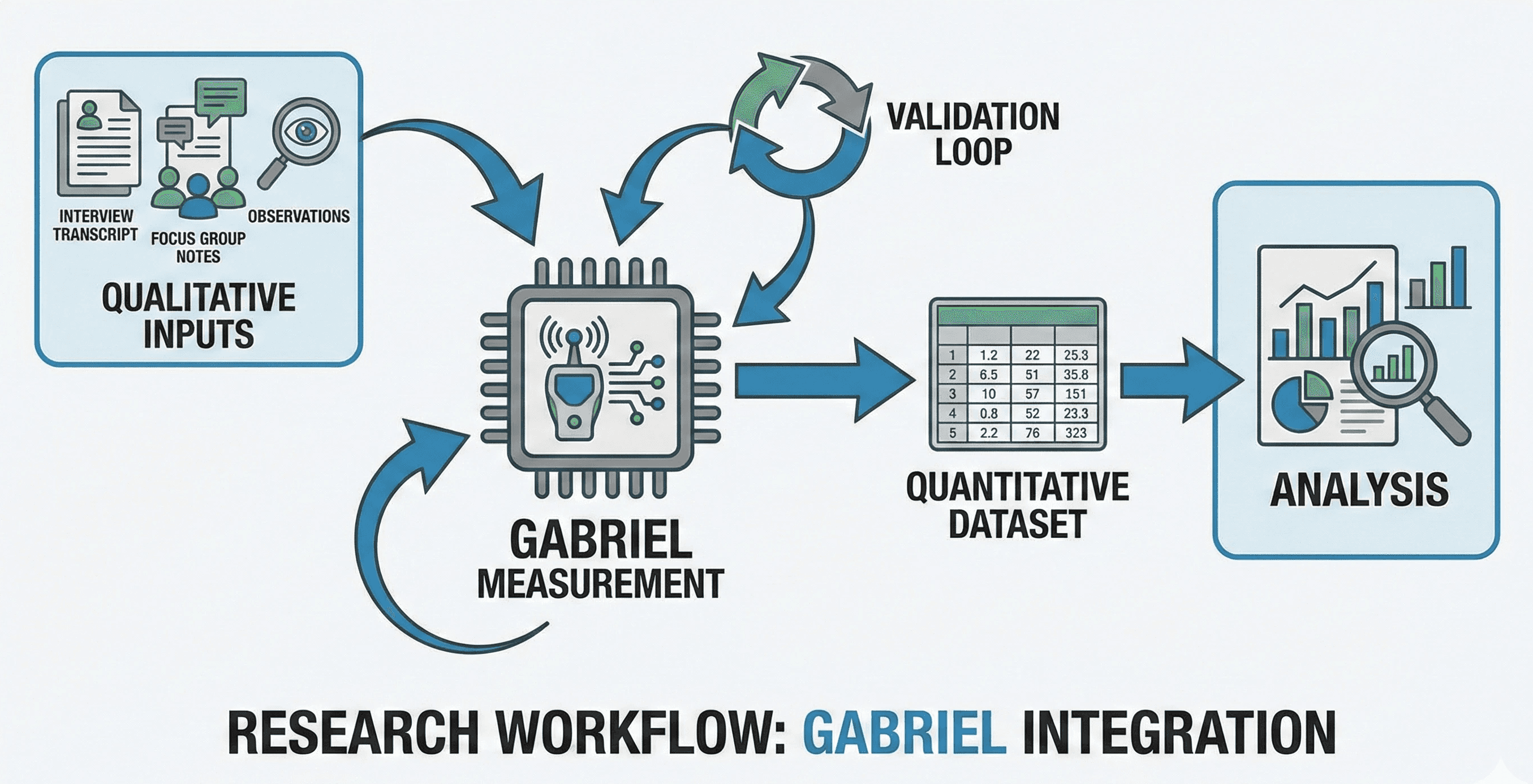
GABRIEL is an open-source toolkit from OpenAI that uses GPT to convert unstructured qualitative material — like text and images — into quantitative measurements. It helps social scientists define what they want to measure, apply consistent labelling at scale, and analyse large datasets faster than manual coding alone.
Qualitative data is rich — interviews, open-ended survey responses, policy documents, images — but it’s also slow to analyse when you’re coding by hand. That bottleneck makes it hard to run studies at the scale modern research questions demand.
GABRIEL is OpenAI’s new open-source toolkit built to close that gap. It uses GPT to help researchers turn unstructured inputs into quantitative measurements that can be analysed statistically, without losing the interpretability that social science requires.
What GABRIEL is (and what it isn’t)
GABRIEL is best thought of as a measurement workflow: you define the attribute you want to quantify (for example, sentiment, policy stance, or “pro‑innovation” framing), then apply that measurement consistently across large volumes of data.
It’s not a magic “auto-truth” button. The value comes from making your coding more scalable and more auditable: you can test prompts, compare results against human labels, and iterate until the measurement behaves the way your study design requires.
What data can it handle?
OpenAI’s announcement focuses on text and images, and the GitHub repository description also notes audio as a supported modality.
That matters because many research datasets aren’t just spreadsheets — they’re mixed-media collections that are hard to quantify without an army of research assistants.
How it works in practice
A practical way to use GABRIEL is to treat it as a structured bridge between qualitative interpretation and quantitative analysis:
Define the construct you want to measure (what “counts” and what doesn’t).
Design a rubric and prompt that captures that construct consistently.
Validate on a small sample (compare against expert labels; check edge cases; refine).
Scale to the full dataset once your measurement is stable.
This approach keeps the research logic in the foreground, while letting the toolkit handle the repeatability and volume that makes manual analysis drag on for months.
Practical examples social scientists can start with
GABRIEL is particularly useful when you need to apply the same judgement many times, such as:
Coding themes or stances across thousands of policy documents
Turning open-ended survey responses into consistent categories
Measuring attributes in mixed datasets (text + images) for comparative studies
Summary
If your research workflow is bottlenecked by manual coding, GABRIEL offers a structured way to scale measurement across qualitative data — while keeping validation and interpretability in view. As an open-source toolkit, it’s accessible to researchers who want to build repeatable, testable measurement pipelines using GPT.
Next steps: Generation Digital can help you assess where GABRIEL fits in your methodology, design evaluation steps, and integrate the workflow into your existing tooling.
FAQs
Q1: How does GABRIEL improve research scalability?
By turning qualitative inputs into repeatable quantitative measurements, it reduces the amount of manual coding required and makes it feasible to analyse much larger datasets.
Q2: What types of data can GABRIEL handle?
OpenAI describes support for text and images, and the repository also mentions audio.
Q3: Is GABRIEL accessible to all researchers?
Yes. It’s released as open-source under the Apache 2.0 licence, so researchers can use and adapt it within the licence terms.
Q4: Does using GABRIEL remove the need for human validation?
No — the accompanying “GPT as a measurement tool” framing emphasises designing the measurement carefully and validating it, especially on a labelled subset, before scaling.
GABRIEL is an open-source toolkit from OpenAI that uses GPT to convert unstructured qualitative material — like text and images — into quantitative measurements. It helps social scientists define what they want to measure, apply consistent labelling at scale, and analyse large datasets faster than manual coding alone.
Qualitative data is rich — interviews, open-ended survey responses, policy documents, images — but it’s also slow to analyse when you’re coding by hand. That bottleneck makes it hard to run studies at the scale modern research questions demand.
GABRIEL is OpenAI’s new open-source toolkit built to close that gap. It uses GPT to help researchers turn unstructured inputs into quantitative measurements that can be analysed statistically, without losing the interpretability that social science requires.
What GABRIEL is (and what it isn’t)
GABRIEL is best thought of as a measurement workflow: you define the attribute you want to quantify (for example, sentiment, policy stance, or “pro‑innovation” framing), then apply that measurement consistently across large volumes of data.
It’s not a magic “auto-truth” button. The value comes from making your coding more scalable and more auditable: you can test prompts, compare results against human labels, and iterate until the measurement behaves the way your study design requires.

What data can it handle?
OpenAI’s announcement focuses on text and images, and the GitHub repository description also notes audio as a supported modality.
That matters because many research datasets aren’t just spreadsheets — they’re mixed-media collections that are hard to quantify without an army of research assistants.
How it works in practice
A practical way to use GABRIEL is to treat it as a structured bridge between qualitative interpretation and quantitative analysis:
Define the construct you want to measure (what “counts” and what doesn’t).
Design a rubric and prompt that captures that construct consistently.
Validate on a small sample (compare against expert labels; check edge cases; refine).
Scale to the full dataset once your measurement is stable.
This approach keeps the research logic in the foreground, while letting the toolkit handle the repeatability and volume that makes manual analysis drag on for months.
Practical examples social scientists can start with
GABRIEL is particularly useful when you need to apply the same judgement many times, such as:
Coding themes or stances across thousands of policy documents
Turning open-ended survey responses into consistent categories
Measuring attributes in mixed datasets (text + images) for comparative studies
Summary
If your research workflow is bottlenecked by manual coding, GABRIEL offers a structured way to scale measurement across qualitative data — while keeping validation and interpretability in view. As an open-source toolkit, it’s accessible to researchers who want to build repeatable, testable measurement pipelines using GPT.
Next steps: Generation Digital can help you assess where GABRIEL fits in your methodology, design evaluation steps, and integrate the workflow into your existing tooling.
FAQs
Q1: How does GABRIEL improve research scalability?
By turning qualitative inputs into repeatable quantitative measurements, it reduces the amount of manual coding required and makes it feasible to analyse much larger datasets.
Q2: What types of data can GABRIEL handle?
OpenAI describes support for text and images, and the repository also mentions audio.
Q3: Is GABRIEL accessible to all researchers?
Yes. It’s released as open-source under the Apache 2.0 licence, so researchers can use and adapt it within the licence terms.
Q4: Does using GABRIEL remove the need for human validation?
No — the accompanying “GPT as a measurement tool” framing emphasises designing the measurement carefully and validating it, especially on a labelled subset, before scaling.
Receive weekly AI news and advice straight to your inbox
By subscribing, you agree to allow Generation Digital to store and process your information according to our privacy policy. You can review the full policy at gend.co/privacy.
Upcoming Workshops and Webinars


Streamlined Operations for Canadian Businesses - Asana
Virtual Webinar
Wednesday, February 25, 2026
Online


Collaborate with AI Team Members - Asana
In-Person Workshop
Thursday, February 26, 2026
Toronto, Canada


From Concept to Prototype - AI in Miro
Online Webinar
Wednesday, February 18, 2026
Online
Generation
Digital

Business Number: 256 9431 77 | Copyright 2026 | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
Generation
Digital










